Using AOP by declaring/annotation in Spring
Categories: Java; Tagged with: AOP • Aspect • Java • Spring; @ June 26th, 2012 23:21Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) complements Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) by providing another way of thinking about program structure. The key unit of modularity in OOP is the class, whereas in AOP the unit of modularity is the aspect. Aspects enable the modularization of concerns such as transaction management that cut across multiple types and objects. (Such concerns are often termed crosscutting concerns in AOP literature.)
Here is a simple example showing the AOP feature in Spring, like the definition of bean, we can use AOP by declaring or annotation. we have a method that can insert a new user into the database, and we want to trace a log by AOP:
/**
* Insert new user using transactionTemplate.
* @param user
*/
public void insertUserByTxTemplate(final User user) {
session.save(user);
}
1. Using AOP by Declaring
First, we need to crate an Aspect class:
package com.liguoliang.spring.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
public class Logging {
public void preLog() {
System.out.println("PreLog...");
}
public void postLog() {
System.out.println("PostLog...");
}
public void aroundLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Around...Logging begin..");
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Around...Logging end...");
}
}
and then, we need define the AOP in spring config file:
<bean id="logging" class="com.liguoliang.spring.aop.Logging"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="logging">
<aop:before pointcut="execution(* com.liguoliang.spring.UserHibernateDAO.insertUserByTxTemplate(..))" method="preLog" />
<aop:after pointcut="execution(* com.liguoliang.spring.UserHibernateDAO.insertUserByTxTemplate(..))" method="postLog" />
<aop:around pointcut="execution(* com.liguoliang.spring.UserHibernateDAO.insertUserByTxTemplate(..))" method="aroundLog" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
And here is the output:
PreLog...
Around...Logging begin..
Exception catched...rollback now...
PostLog...
Around...Logging end...
2. Using Annotation.
We can define the pointcut and advices in the aspect class:
package com.liguoliang.spring.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAnnotation {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.liguoliang.spring.UserHibernateDAO.insertUserByTxTemplate(..))")
public void newUser() {
}
@Before("newUser()")
public void preLog() {
System.out.println("[Annotation] PreLog...");
}
@After("newUser()")
public void postLog() {
System.out.println("[Annotation] PostLog...");
}
@Around("newUser()")
public void aroundLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Annotation] Around...Logging begin..");
try {
joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("[Annotation] Around...Logging end...");
}
}
Because all configuration info is sorted in this class, so the spring config file is different:
<bean id="loggingAnnotation" class="com.liguoliang.spring.aop.LoggingAnnotation"></bean>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
and here is the output:
[Annotation] PreLog...
[Annotation] Around...Logging begin..
Exception catched...rollback now...
[Annotation] PostLog...
[Annotation] Around...Logging end...
Transaction management using Spring and Hibernate
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Hibernate • Java • Spring • Transaction • TransactionTemplate; @ June 26th, 2012 22:07Spring doesn’t directly manage transactions, it comes with a selection of transaction managers, such as: DataSourceTransactionManager, HibernateTransactionManager, JpaTransactionManager etc,.
There are two way to manage transaction in Spring: based on programming or configuration. no matter which way we choose, we always need to define the beans needed:
Declaring transactions
Here we define a transactionManager using hibernateTransactionManager, and a transaction template:
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="globalRollbackOnParticipationFailure" value="false" />
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
<bean id="txTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property>
</bean>
‘sessionFactory’ bean configuration: http://liguoliang.com/2012/using-spring-jdbc-template/
And now, I’ll show you the the two transaction management ways:
1. by Programming
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate txTemplate;
/**
* Insert new user using transactionTemplate.
* @param user
*/
public void insertUserByTxTemplate(final User user) {
txTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback() {
@Override
public Void doInTransaction(TransactionStatus txStatus) {
try {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
session.save(user);
throw new RuntimeException("Exception throwed!");
} catch (Exception e) {
txStatus.setRollbackOnly();
}
return null;
}
});
}
Manage transaction using txTemplate.execute().
2. by Configuration/Declaring
using annotation
/**
* Insert new user using transaction manager.
* @param user
*/
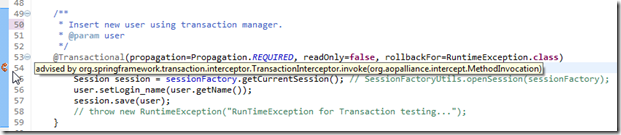
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED, readOnly=false, rollbackFor=RuntimeException.class)
public void insertUser(User user) {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession(); // SessionFactoryUtils.openSession(sessionFactory);
user.setLogin_name(user.getName());
session.save(user);
// throw new RuntimeException("RunTimeException for Transaction testing...");
}
If you are using STS(SpringSource tool suite) you can see there is an indicator:
About transaction rollback
- by default: if there is a runtime exception (UnChecked exception), will rollback;
- If rollback failed, check the @Transactional, and the method: if you get session by SessionFactoryUtils.openSession(sessionFactory),, rollback will failed – I think only sessionFactory.getCurrentSession() can work.
Links:
Spring Transaction – automatic rollback of previous db updates when one db update failes
Spring’s @Transactional does not rollback on checked exceptions
Transaction strategies: Understanding transaction pitfalls
Using Spring JDBC Template
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Java • JDBC • JDBCTemplate • Spring; @ June 25th, 2012 21:48JDBCTemplate simplifies the use of JDBC and helps to avoid common errors. It executes core JDBC workflow, leaving application code to provide SQL and extract results.
http://static.springsource.org/spring/docs/2.0.x/api/org/springframework/jdbc/core/JdbcTemplate.html
Here are two methods, the 2nd one is using JDBCTemplate from Srping, you can see the code are more simple and clear:
/** * LoadUsers using JDBC. * @param dataSource * @return */ public ListloadUserJDBC(DataSource dataSource) { List users = new ArrayList (); Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT ID, EMAIL, LOGIN_NAME, NAME FROM ACCT_USER"); ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { User user = new User(); users.add(user); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); System.out.println(user); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } return users; } /** * Load users using Spring JDBCTemplate. * @param jdbcTemplate * @return */ public java.util.List doJDBCTempQuery(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { String queryUsers = "SELECT ID, EMAIL, LOGIN_NAME, NAME FROM ACCT_USER"; java.util.List users = jdbcTemplate.query(queryUsers, new ParameterizedRowMapper () { @Override public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException { User user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt(1)); user.setName(rs.getString(4)); return user; } }); return users; }
And here is a example to define the template bean:
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/mini-liguoliang.com" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="pw" />
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
Spirng3.1 + Hibernate4.1 HelloWorld
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Hibernate • Java • Spring • SSH; @ June 24th, 2012 23:20Here is a simple example about configuration of Spring3 and Hibernate4.
1. We need define a sessionFactory bean:
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost/mini-liguoliang.com" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="password" />
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="packagesToScan" value="com.liguoliang.spring.po"></property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.liguoliang.spring"></context:component-scan>
Basically, we did there things:
- Define the datasource;
- define the session factory, we need specify the packagesToScan property, this property will scan all entity annotated class.
- define the context component-scan basepackage, this will scan all @Repository annotated Class, like the dao class in 4.
2. Define the Entity Class:
package com.liguoliang.spring.po;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
@Entity
@javax.persistence.Table(name="ACCT_USER")
public class User {
@javax.persistence.Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
private String login_name;
public String getLogin_name() {
return login_name;
}
public void setLogin_name(String login_name) {
this.login_name = login_name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String toString() {
return "User - " + name + " [" + id + "]";
}
}
Note the annotation: @Entity
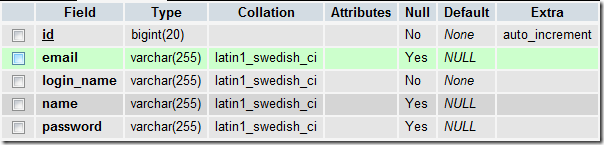
3. We have a table related to this entity:
4. In the dao class:
package com.liguoliang.spring;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.SessionFactoryUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.liguoliang.spring.po.User;
@Repository
public class UserHibernateDAO {
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
@Autowired
public UserHibernateDAO(SessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
}
public User getUserByID(int id) {
Session session = SessionFactoryUtils.openSession(sessionFactory);
return (User) session.get(User.class, id);
}
}
5. Communicate with database using DAO
We need a hibernateBean instance:
package com.liguoliang.spring.web;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/spring/user")
public class ControllerUser {
@Autowired
private UserHibernateDAO userHibernateDAO;
@RequestMapping(value={"", "list"})
public String list(Model model) {
// We just print the user info in the console.
System.out.println("userName: " + userHibernateDAO.getUserByID(10).toString());
return "userList";
}
}
When list() is called, user with the id ’10’ will be loaded by the hibernateDAO, and printed in the console.
6. Related pattern – Data Access Object
http://java.sun.com/blueprints/corej2eepatterns/Patterns/DataAccessObject.html

Figure 9.2 Data Access Object sequence diagram
BusinessObject
The BusinessObject represents the data client. It is the object that requires access to the data source to obtain and store data. A BusinessObject may be implemented as a session bean, entity bean, or some other Java object, in addition to a servlet or helper bean that accesses the data source.
DataAccessObject
The DataAccessObject is the primary object of this pattern. The DataAccessObject abstracts the underlying data access implementation for the BusinessObject to enable transparent access to the data source. The BusinessObject also delegates data load and store operations to the DataAccessObject.
DataSource
This represents a data source implementation. A data source could be a database such as an RDBMS, OODBMS, XML repository, flat file system, and so forth. A data source can also be another system (legacy/mainframe), service (B2B service or credit card bureau), or some kind of repository (LDAP).
TransferObject
This represents a Transfer Object used as a data carrier. The DataAccessObject may use a Transfer Object to return data to the client. The DataAccessObject may also receive the data from the client in a Transfer Object to update the data in the data source.
Using Inner class in Java
Categories: Java; Tagged with: InnerClass • Java • NestedClass; @ May 22nd, 2012 1:03Here is the code:
package innerClasds.scjp.liguoliang.com;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class TestInnerClass {
private String name = "var+TestName";
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestInnerClass().new InnerClass().printDes();
new TestInnerClass().testInnerClassInMethod("info");
TestInnerClass.StaticClass.printInfo();
}
/**
* 2. Inner class in method.
*/
void testInnerClassInMethod(final String info) {
// In this class, we can get any variable in the outer class, but only can access the final variables in the method.
// The reason is(from scjp book): can not keep variables(stored in stack) can keep as long as inner class instance (stored in the heap),
// so the inner class only access the final variable.
// and the class access modifier: only abstract or final is permitted
abstract class InnerClassInMethod {
abstract void printInfo();
}
/** 3. Anonymous class; */
InnerClassInMethod inMethod = new InnerClassInMethod() {
void printInfo() {
System.out.println(InnerClassInMethod.class + TestInnerClass.this.name + "__" + info);
}
};
inMethod.printInfo();
}
/**
* 1. Normal inner class. can use public, protected, (default), private accessor modifier to control the scope of the class.
* @author Li Guoliang
*
*/
private class InnerClass extends TestInnerClass implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//always need final, otherwise:
// The field s cannot be declared static; static fields can only be declared in static or top level types
public static final String s = "s";
void printDes() {
System.out.println("Inner" + s + " " + TestInnerClass.class);
}
}
/**
* 4. Static nested class.
* @author Li Guoliang
*
*/
private static class StaticClass {
static void printInfo() {
System.out.println(StaticClass.class);
}
}
}
Some comments:
1. Inner Class:
can be public, protected, private, final, abstract, static, strictfp.
need an outer instance to crate the inner instance, like: new TestInnerClass().new InnerClass();
Use outClass.this to get the outer instance;
2. Inner class in method
can be public, protected, private, final, abstract, static, strictfp;
can access any property in the outer instance;
only can access final variable in the method.
3. Anonymous class
4. Static nested class
can be public, protected, private, final, abstract, static, strictfp.
here are some notes when I first learn inner class in java: >>go<<